CVE-2021-31802 NETGEAR R7000 httpd PreAuth RCE
TL;DR
CVE-2021-31802 is my first CVE assignment, Thanks @d4rkn3ss for his brilliant work. I learn a lot from his work. Thanks @SecuriTeam_SSD for their professional work, they help me to get the CVE assignment within a month, which I never got a response from MITRE by myself.
Vulnerability Summary
This vulnerability allows network-adjacent attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of NETGEAR R7000 routers. Authentication is not required to exploit this vulnerability.
The vulnerability exists within the handling of http request, the issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result a heap overflow. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code with the root privilege.
Affected Systems
Netgear Nighthawk R7000 running firmware version 1.0.11.116 and before
Vulnerability Root Cause Analysis
I bypass the patch for the ZDI-20-709 vulnerability, so I get this vulnerability. The patch for ZDI-20-709 cannot solve the root cause of the vulnerability. The httpd program allows user to upload a file with the url /backup.cgi. While the root cause of the vulnerability is that the program uses two variables to represent the length of the uploaded file.
One variable is related to the value of the Content-length in the http post request header, the other one is the length of the file content in the http post request body.
The vulnerability exists in the sub_16674. Below picture is the heap overflow point: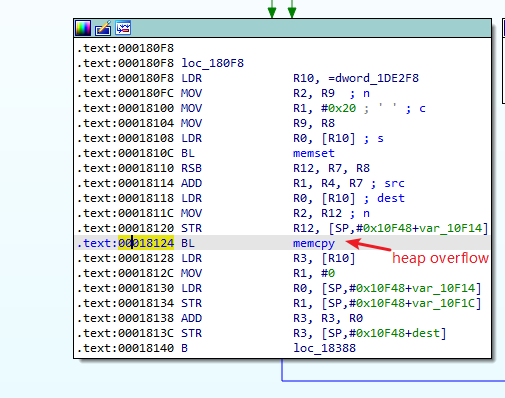
The decompiled code is like this: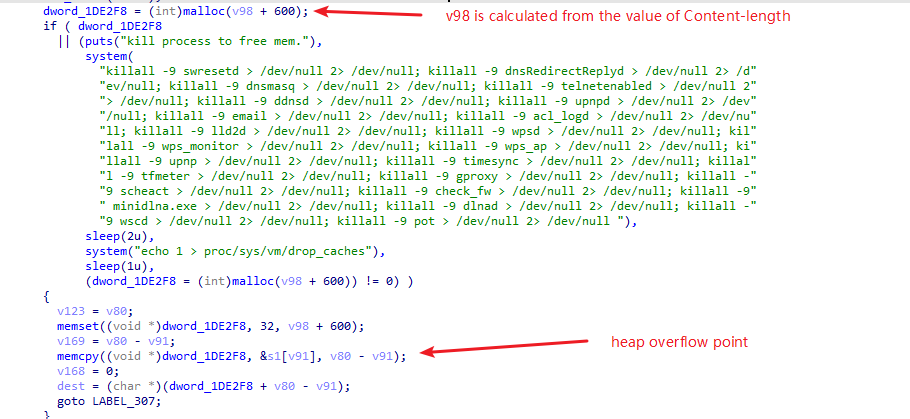
The program allocates memory for storing the file content by calling malloc,the return value is stored by dword_1DE2F8, the size is the value of Content-Length plus 600. The Content-Length value can be controlled by the attacker, thus if we provide a proper value, we can make the malloc to return any size of the heap chunk we want.
The memcpy function copies the http request payload from s1 to dword_1DE2F8, the copied buffer length is v80 - v91 which is the length of the file content in the http post request body.
So this is the problem, the size of the heap-based buffer dword_1DE2F8 can by controlled by the attacker with a small value, and the v80-v91 can also by controlled with another larger value. Thus, it can cause a heap overflow.
Exploit Considerations
The patch for ZDI-20-709 is that it adds a check for one byte before Content-Length, it checks if it is a '\n', I simply add a '\n' before the Content-Length in order to bypass the patch. Though the vulnerabilities are basically the same, but the exploit still needs a lot of efforts because the heap states are different between R6700 and R7000.
We may conduct a fastbin dup attack to the heap overflow vulnerability. But it is not easy to do this. Fastbin dup attack needs two continuous malloc function to get two return address from a same fastbin list, the first malloc returns the chunk whose fd pointer is overwritten by the heap overflow, the second malloc returns the address where we want to write data.
The bigest problem is that there should be no free procedure between these two malloc functions. But dword_1DE2F8 is checked every time before malloc: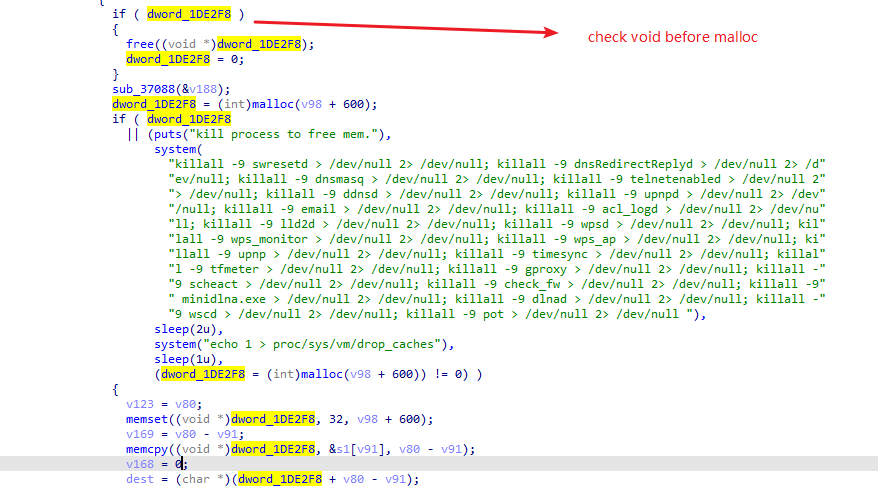
If dword_1DE2F8 is not a null pointer, it will be freed and set 0. Thus we should find another point of calling malloc.
Luckily, there is another malloc whose size can by controlled by us, it is in the function of sub_A5B68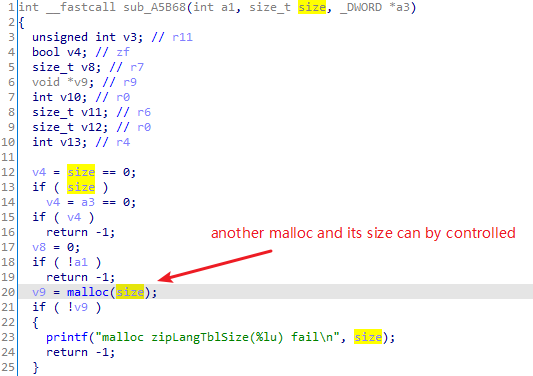
The function handles another file upload http request, we may use the /genierestore.cgi to trigger this function.
But there is another problem, both /genierestore.cgi and /backup.cgi requests can cause the fopen function gets called. The fopen function will call malloc(0x60) and mallloc(0x1000). malloc(0x1000) will cause __malloc_consolidate function gets called which will destroy the fastbin, since the size is larger than the value of max_fast.
We need to find a way to change the max_fast value to a large value so that the __malloc_consolidate will not be triggered. According to the implemenation of uClibc free function:
1 | if ((unsigned long)(size) <= (unsigned long)(av->max_fast) |
When we free a chunk whose size is 0x8, fastbin_index(size) return -1, and av->fastbins[fastbin_index(size)] will cause an out-of-bounds access.
1 | struct malloc_state { |
According to the struct of malloc_state, fb = &(av->fastbins[-1]) exactly points to max_fast, thus *fb = p will make the max_fast to a large value.
But in the normal situation, the chunk size cannot be 0x8 bytes, because it means that the user data is 0 byte. So we can first make use of the heap overflow vulnerability to overwrite the PREV_INUSE flag of a chunk so that it incorrectly indicates that the previous chunk is free. Due to the incorrect PREV_INUSE flag, we can get malloc() to return a chunk that overlaps an actual existing chunk. This lets us edit the size field in the existing chunk’s metadata, setting it to the invalid value of 8. When this chunk is freed and placed on the fastbin, malloc_stats->max_fast is overwritten by a large value.Then the fopen will not lead to a __malloc_consolidate, so we can conduct a fastbin dup attack.
Once we make the malloc return a chosen address, we could overwrite the GOT entry of the free to the address of system PLT code. Finally we execute utelnetd -l /bin/sh to start the telnet service, then we get the root shell of R7000.
I use some techniques to make the exploit more steady.
To make the malloc chunks are adjacent so that the heap overflow will not corrupt other heap-based buffers, I send a very long payload to trigger closing the tcp connection in advance so that the
/backup.cgirequest will not callingfopensubsequently, and there will be no other malloc calling between two http requests.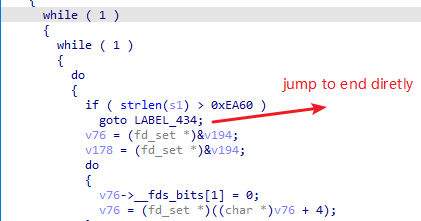
The httpd program’s heap state may be different when user login or logout the web management, to make the heap state consistent,I find that when I try to login the web management with wrong password for 3 times, the httpd program will redirect the user to a
Router Password Resetpage. I can make use of this feature to achieve a steady heap state.